Table of Contents
Togglestainless steel 316 metal powder offers unique advantages for additive manufacturing and industrial applications requiring excellent corrosion resistance, hardness, and high temperature strength. This guide provides engineers, designers, and procurement specialists a comprehensive overview of 316 powder metallurgy compositions, properties, specifications, pricing, applications, pros/cons comparisons and FAQs.
Introduction to stainless steel 316 metal powder
stainless steel 316 metal powder revolutionizes production through capabilities like:
- Custom alloys creation
- Complex shape fabrication
- Superior part properties
Common grades used include:
- 316L – Low carbon variant for improved weldability & machinability
- 316H – Higher carbon content for enhanced yield and tensile strength
This guide covers factors when selecting 316 powder:
- Alloy Composition and Powder Characteristics
- Mechanical Properties, Strength Levels
- Particle Size Distribution Specifications
- Test Certificate Data Sheet Requirements
- Pricing Models For Volume Orders
- High Temperature and Corrosion Resistance
- Pros vs Cons Compared to Solid Barstock
- FAQs on Sourcing, Quality Control and Applications
Table 1 overviews 316 metal powder types and applications. Recommendations are provided based on industry insights. Let us explore in detail…
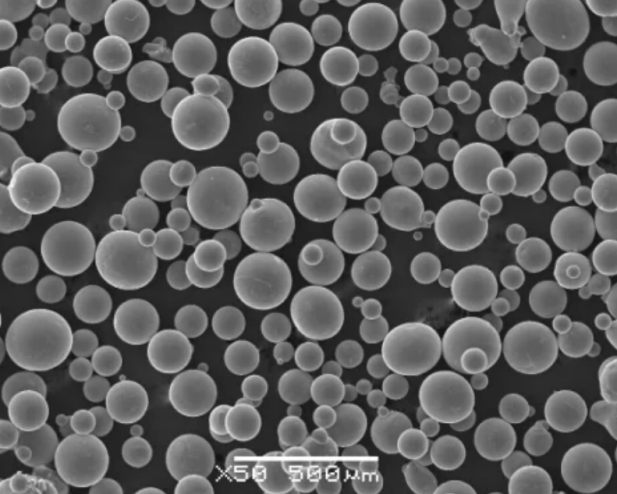
stainless steel 316 metal powder Compositions
Table 2 shows 316 stainless steel powder compositions with elemental chemical analysis critical for materials performance. Slight variations differentiate grades.
| Element | 316L SS (%wt) | 316H SS (%wt) |
|---|---|---|
| Chromium (Cr) | 16.5 – 18.5 | 16.5 – 18.5 |
| Nickel (Ni) | 10.0 – 14.0 | 10.0 – 14.0 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 2.0 – 3.0 | 2.0 – 3.0 |
| Silicon (Si) | 0.0 – 1.0 | 0.0 – 1.0 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0.0 – 2.0 | 0.0 – 2.0 |
| Carbon (C) | 0.03 max | 0.04 – 0.10 |
| Phosphorus (P) | 0.045 max | 0.045 max |
| Sulfur (S) | 0.030 max | 0.030 max |
| Iron (Fe) | Balance | Balance |
The molybdenum boosts corrosion resistance. Lower carbon in 316L enhances weldability. Higher 0.04-0.10% carbon in 316H increases strength.
Powder production methods also affect properties:
- Water Atomization for superior powder shape and flowability
- Gas Atomization for smaller, uniform particle distributions
- Plasma rotating electrode process (PREP) powders offer higher densities and repeatable spherical morphology.
Mechanical Properties and Strength Levels
Table 3 shows 316 stainless steel powder meets or exceeds mechanical properties versus cast or wrought equivalents. This facilitates high performance part production.
| Mechanical Property | 316L SS Typical | 316H SS Typical |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength, Ultimate (MPa) | ≥485 | ≥580 |
| Tensile Strength, Yield (MPa) | ≥170 | ≥290 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | ≥40 | ≥35 |
| Hardness (HRB) | ≥ 80 | ≥90 |
Superior tensile and yield strengths from 316H powder enable lightweighting and resilience across load-bearing components. Ductility levels prevent premature brittle failure. Hardness confers enhanced wear resistance during use.
These properties depend strongly on particle morphology, size uniformity, phases and impurities. Rigorously inspect certifications on powder quality.
stainless steel 316 metal powder Particle Size Specs
Table 4 shows common 316 stainless steel powder size distributions. Size range and shape affect part density and quality:
| Mesh Size | Micron Range | ASTM Size Name |
|---|---|---|
| -140+325 | 44-105 | Extra Fine |
| -325 | 0-45 | Superfine |
| -100+325 | 149-45 | Submicron |
- Smallest particle sizes allow greatest resolution and accuracy.
- Normal size distributions maintain flowability.
- Water atomization enables consistent shape for higher densities.
Powders spread during printing should have mean size between 15-45 microns for optimal packing and spreadability.
Use higher resolution scans and printers to gain full advantage of superfine or submicron particles during fabrication.
Powder Test Certificate Requirements
All 316 stainless steel powder lots require full certification with test reports indicating:
- Chemical composition by %weight
- Particle size distribution with mesh passing percentages
- True density g/cm3 and apparent density g/cm3 data
- Flow rate in Hall flowmeter seconds
- SEM micrograph showing shape and morphology
- Mechanical properties test data
- Production lot number and date
Carefully review to ensure stringent QC and the ability to trace any raw defect back through manufacturing records.
Pricing Models For Volume Metal Powder Orders
Table 5 outlines rough 316 stainless steel powder pricing at different volumes under typical market conditions:
| Order Quantity | Price Estimate |
|---|---|
| 10 kg | $100+/kg |
| 100 kg | $50+/kg |
| 500 kg | $30+/kg |
| 1000+ kg | subkey pricing |
Bulk discounts apply for over 500-1000 kg based on long term agreements. Actual pricing fluctuates with commodity indexes.
Upcharges: Special packaging, testing, certifications, fast delivery, prototype lots.
Cost Savings: Standard alloys using stock powder inventory rather than custom materials.
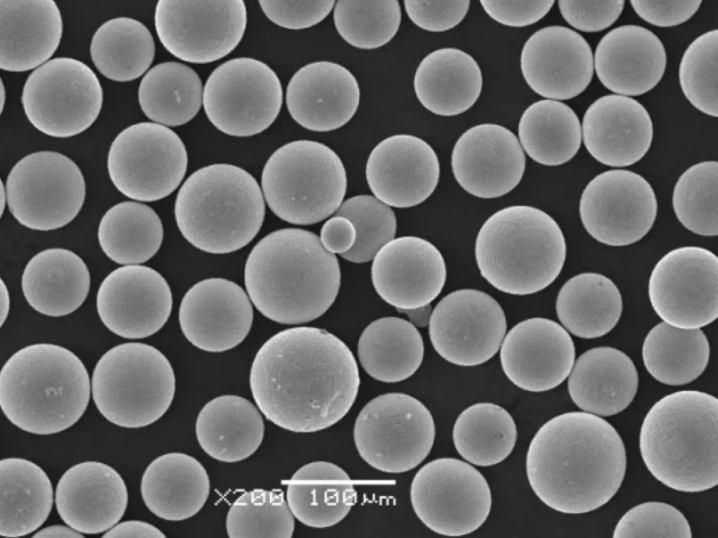
stainless steel 316 metal powder Corrosion and Temperature Resistance
316L and 316H powders offer exceptional corrosion and oxidation resistance comparable/superior to wrought products, making them ideal for:
Table 6
| Environment | Max Service Temperature |
|---|---|
| Acids, Alkalis | 593°C / 1100°F |
| Organic Chemicals | 343°C / 650°F |
| Oxidation Resistance | 870°C / 1600°F |
| Sulfuric Acid | 149°C / 300°F |
The austenitic FCC crystal structure, additions like molybdenum and low impurity levels enable such resistance. Ion bombarding exposed surfaces using powder bed fusion machines further enhances corrosion protection.
Pros vs Cons: stainless steel 316 metal powder vs Solid Barstock
Table 7
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|
| 316 SS Metal Powder | Complex shapes, advanced properties | Higher cost, quality control |
| Custom alloys, densities | Post-processing needed | |
| Innovative geometries, weight savings | Powder handling challenges | |
| 316 SS Solid Barstock | Lower piece cost, ease of machining | Shape and geometry limits |
| Forgings have enhanced properties | Much heavier parts | |
| Readily available | Significant material waste |
In general, 316 stainless steel powder justifies premiums for low volume complex components where advanced properties are vital. Barstock offers affordability for simple shapes in high volumes.
By combining both material forms across long term roadmaps, overall costs can be optimized.
FAQ
Table 8 – Common metal powder selection queries:
| FAQ | Answer |
|---|---|
| Should I request test reports? | Yes, review all certs to confirm powder quality |
| What size powder particles should I use? | 15-45u ideal, depends on printer resolution |
| Which process offers better consistency? | Water atomization or PREP both reliable |
| How much stock should I buy upfront? | Start small, buy more once printer qualified |
| What factors affect density? | Particle morphology, size distribution, alloy purity all key |
Table 9 – Application-specific metal powder advice:
| FAQ | Answer |
|---|---|
| Is 316L or 316H better for ocean applications? | 316L has superior corrosion performance |
| Which powder maximizes high hardness? | 316H achieves over HRB 90 in aged condition |
| What is the easiest way to achieve complex geometries? | Design the part in CAD then print in 316 powder |
| How should I adjust alloy composition for improving wear resistance? | Increase hardness through higher carbon 316H powder |
| What post-processing improves surface finishes? | Try media tumbling rather than chemically finishing printed surfaces |