Table of Contents
ToggleNickel-Based Powder, a fine, metallic dust, might seem insignificant at first glance. But don’t be fooled by its size! This unassuming material plays a critical role in various industries, from aerospace and electronics to medicine and energy.
Nickel powder’s magic lies in its unique properties. It boasts excellent strength, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature performance. These qualities make it a versatile building block for countless applications. However, creating this wonder material requires specific techniques. So, buckle up as we delve into the world of nickel powder production methods and explore some of the most popular metal powder models!
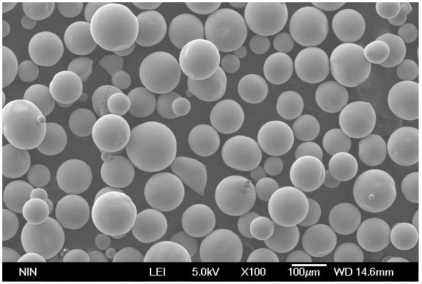
Production Methods of Nickel-Based Powder
Nickel powder isn’t magically conjured up. It’s meticulously crafted through various processes, each with its own advantages and limitations. Here’s a closer look at the three main methods:
- Electrolytic Nickel Powder: Imagine a nickel-plated teacup slowly dissolving into tiny flakes. That’s essentially what happens in electrolytic nickel powder production. Nickel anodes are submerged in an electrolyte solution, and an electric current gently pulls nickel ions from the anode, depositing them as fine flakes on the cathode. This method yields highly pure nickel powder, but the flakes can be irregular in shape, impacting packing density and flowability.
- Reduced Nickel Powder: This method involves a chemical dance between nickel compounds and reducing agents like hydrogen. Nickel oxides or sulfides are heated in a hydrogen atmosphere, where the reducing agent steals oxygen atoms from the nickel compound, leaving behind pure nickel powder. Reduced nickel powder offers good flowability and spherical shapes, making it ideal for additive manufacturing processes like 3D printing.
- Atomized Nickel Powder: Picture molten nickel raining down and solidifying into tiny droplets. That’s the essence of atomization. Molten nickel is poured through a high-pressure nozzle, breaking it into a fine mist. This mist is then rapidly cooled with a stream of gas or water, solidifying the nickel droplets into spherical powder. Atomized nickel powder boasts excellent control over particle size and shape, making it perfect for high-performance applications like jet engine components.
Table 1: Comparison of Nickel Powder Production Methods
| Feature | Electrolytic Nickel Powder | Reduced Nickel Powder | Atomized Nickel Powder |
|---|---|---|---|
| Process | Electrolysis | Chemical reduction | Molten metal atomization |
| Powder Morphology | Flakes | Spherical | Spherical |
| Purity | High | Moderate to High | High |
| Flowability | Moderate | Good | Excellent |
| Applications | Battery electrodes, catalysts | Additive manufacturing, brazing | Jet engine components, filters |
Choosing the Right Method: The best production method for nickel powder depends on the desired properties and application. For instance, if high purity is paramount, electrolytic nickel powder might be ideal. For 3D printing, the excellent flowability of reduced nickel powder is crucial. Finally, for demanding applications like jet engine components, the precise control offered by atomized nickel powder reigns supreme.
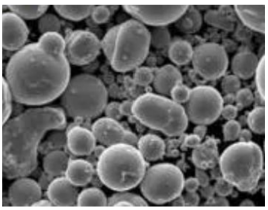
Top 10 Metal Powder Models
Now that we understand the production methods, let’s explore some of the most popular nickel powder models in the market:
- INCO® Nickel Powders (Vale): A household name in the nickel world, INCO® powders offer a range of purities and particle sizes, catering to diverse applications like battery electrodes and catalysts. Renowned for their consistency and high quality, these powders are a trusted choice for many manufacturers.
- Höganäs Spherical Nickel Powders (Höganäs AB): Imagine tiny, near-perfect spheres of nickel. That’s what Höganäs brings to the table. Their atomized nickel powders boast excellent flowability and packing density, making them ideal for applications demanding precise control over material properties.
- AMPC Nickel Powders (American Elements): For those seeking high-purity nickel powder specifically tailored for additive manufacturing, AMPC powders are a top contender. Offered in various particle sizes, these powders ensure smooth printing processes and excellent final product properties.
- Sherritt International’s HP Nickel Powder: Imagine nickel powder specifically designed for high-performance applications. Sherritt International delivers just that with their HP Nickel Powder. This atomized powder boasts exceptional high-temperature capabilities and strength, making it a perfect fit for demanding environments like jet engines and gas turbines.
- BASF INOBlend® Nickel Powders: Sometimes, blending different materials can create a winning combination. BASF understands this with their INOBlend® Nickel Powders. These innovative powders combine nickel with other elements to achieve specific properties.
- Carpenter Additive Nickel Powders (Carpenter Technology Corporation): When it comes to pushing the boundaries of additive manufacturing, Carpenter Technology Corporation steps up with their Carpenter Additive Nickel Powders. These powders are specifically designed for 3D printing processes, offering excellent printability and exceptional mechanical properties for creating high-strength components.
- Sandvik Osprey® Nickel Powders (Sandvik AB): Imagine nickel powder trusted for aerospace applications. That’s the reputation of Sandvik Osprey® Nickel Powders. Produced via gas atomization, these powders offer exceptional purity, consistent morphology, and superior high-temperature performance, making them ideal for crafting jet engine components and other demanding aerospace parts.
- LPFW Nickel Powders (LPFW GmbH): Looking for a reliable and versatile nickel powder supplier? Look no further than LPFW GmbH. Their nickel powders cater to a wide range of applications, from battery electrodes and catalysts to brazing and metal injection molding (MIM). With a focus on quality and consistency, LPFW powders are a popular choice for manufacturers seeking dependable performance.
- MicroPowders Nickel Powders (MicroPowders Inc.): Sometimes, size truly matters. MicroPowders understands this and offers a range of ultra-fine nickel powders. These submicron powders are perfect for applications requiring a high surface area, such as fuel cells and catalysts. Their small size allows for increased reaction rates and improved efficiency.
- Sumitomo Metal Industries Nickel Powders (Sumitomo Metal Industries, Ltd.): From Japan comes another major player in the nickel powder market – Sumitomo Metal Industries. Their nickel powders are known for their high purity and excellent flowability. They cater to various applications, including electronics, brazing, and additive manufacturing.

Table 2: Key Features of Top 10 Metal Powder Models
| Feature | INCO® Nickel Powders (Vale) | Höganäs Spherical Nickel Powders (Höganäs AB) | AMPC Nickel Powders (American Elements) | Sherritt International’s HP Nickel Powder | BASF INOBlend® Nickel Powders | Carpenter Additive Nickel Powders (Carpenter Technology Corporation) | Sandvik Osprey® Nickel Powders (Sandvik AB) | LPFW Nickel Powders (LPFW GmbH) | MicroPowders Nickel Powders (MicroPowders Inc.) | Sumitomo Metal Industries Nickel Powders (Sumitomo Metal Industries, Ltd.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Production Method | Electrolytic, Reduction | Atomization | Reduction | Atomization | Blending, Atomization | Atomization | Atomization | Various | Various | Atomization |
| Particle Morphology | Flakes | Spherical | Spherical | Spherical | Varies | Spherical | Spherical | Varies | Varies | Spherical |
| Purity | High | High | High | High | Varies | High | High | Moderate to High | High | High |
| Flowability | Moderate | Excellent | Good | Excellent | Varies | Excellent | Excellent | Moderate to Good | Varies | Excellent |
| Applications | Battery electrodes, catalysts | Additive manufacturing, brazing | Additive manufacturing | Jet engine components, filters | Diverse applications | Additive manufacturing | Aerospace components | Diverse applications | Fuel cells, catalysts | Electronics, brazing, additive manufacturing |
A Buyer’s Guide: Choosing the right nickel powder model depends on your specific needs. Consider factors like:
- Application: What will the nickel powder be used for? Different applications require different properties.
- Purity: How important is the purity of the nickel powder? Higher purity often comes at a higher cost.
- Particle Size and Morphology: The size and shape of the nickel powder particles can significantly impact flowability, packing density, and final product properties.
- Flowability: How easily does the powder flow? This is crucial for processes like additive manufacturing.
- Cost: Nickel powder prices can vary depending on the production method, purity, and particle size.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring the Future of Nickel Powders
The world of nickel powders is constantly evolving. Researchers are exploring new production methods to create powders with even better properties. Additionally, there’s a growing focus on developing powders specifically designed for additive manufacturing, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with 3D printing technology. As these advancements unfold, nickel powders are poised to play an even greater role in shaping the future of various industries.

FAQ
Table 3: Frequently Asked Questions about Nickel Powder
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What are the benefits of using nickel powder? | Nickel powder offers several advantages, including high strength, corrosion resistance, good electrical conductivity, and high-temperature performance. These properties make it a versatile material for various applications. |
| What are some of the common applications of nickel powder? | Nickel powder finds use in a wide range of industries, including: * Battery electrodes: Nickel powder is a crucial component of lithium-ion batteries, which power our laptops, smartphones, and electric vehicles. * Additive manufacturing (3D printing): Nickel powder is increasingly used in 3D printing to create complex, high-strength components for aerospace, automotive, and medical applications. * Catalysts: Nickel powder acts as a catalyst in various chemical reactions, accelerating processes in industries like petroleum refining and chemical production. * Electroplating: Nickel powder can be used to create coatings on other materials, improving their corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity. * Brazing: Nickel powder is used in brazing alloys to join together different metals. * Metal injection molding (MIM): Nickel powder is a key ingredient in MIM, a process for creating complex, near-net-shape metal parts. * Filters: Nickel powder can be used to create filters for applications like air and water purification. |
| What are the safety considerations when handling nickel powder? | Nickel powder can be irritating to the skin and lungs. It’s important to follow proper safety precautions when handling nickel powder, including wearing gloves, eye protection, and a respirator. |
| How can I store nickel powder safely? | Nickel powder should be stored in a cool, dry place away from heat, light, and moisture. It’s also important to keep the powder container sealed to prevent contamination. |
| What is the future outlook for the nickel powder market? | The nickel powder market is expected to grow steadily in the coming years, driven by the increasing demand for lithium-ion batteries, additive manufacturing, and other advanced applications. Research and development efforts are focused on creating new nickel powder varieties with improved properties and functionalities, further expanding the potential applications of this versatile material. |
In Conclusion
Nickel powder, though seemingly insignificant at first glance, is a powerhouse material shaping various industries. From the batteries in our pockets to the jet engines soaring through the skies, nickel powder plays a vital role in our modern world. As technology continues to evolve, the future of nickel powder looks bright, with even more innovative applications waiting to be explored. So, the next time you hold your smartphone or witness a plane take off, remember the tiny, yet mighty, nickel powder playing its part behind the scenes.