Table of Contents
ToggleCopper alloy powder refers to powder made from a combination of copper and other alloying elements to produce materials with specialized properties. This powder can be used to manufacture high-performance parts via powder metallurgy techniques like pressing and sintering or additive manufacturing.
Overview of Copper Alloy Powder
Copper alloys are some of the most widely used engineering materials due to their exceptional combination of strength, conductivity, corrosion resistance, machinability, and other properties. By blending copper with alloying elements like zinc, tin, nickel, silicon, aluminum and others, a wide range blends can be created with characteristics finely tuned to specific applications.
Powder metallurgy utilizes fine copper alloy powders which can be compacted into complex parts and sintered for use in industries like automotive, electrical, electronics, industrial machinery etc. The rapid solidification rates during powder atomization allow mixing of immiscible elements and formation of unique microstructures not possible with ingot metallurgy.
Some of the reasons for preference of copper alloy powder are:
- Excellent control of chemical composition in mixed powders
- Refinement of microstructure by rapid solidification
- Ability to produce porous and controlled density parts
- Simpler processing to manufacture intricate shapes
- Prevention of segregation which is common during ingot casting
- Significant cost savings due to material, energy and labor reduction
Advanced additive manufacturing uses the latest metal powders to 3D print sophisticated components with finer grain size and mechanical properties exceeding that of traditional methods.
Types of Copper Alloy Powders
Copper can be alloyed with a range of elements to create materials suitable for diverse applications. Some common powders include:
| Type | Composition |
|---|---|
| Brass | Copper-Zinc (Cu-Zn) |
| Bronze | Copper-Tin (Cu-Sn) |
| Cupronickel | Copper-Nickel (Cu-Ni) |
| Copper-iron | Copper-Iron (Cu-Fe) |
| Copper beryllium | Copper-Beryllium (Cu-Be) |
These base powders can be further modified by adding small amounts of other elements like chromium, silicon, cobalt etc. for enhanced properties. The composition directly influences characteristics like strength, corrosion resistance, wear resistance, thermal properties, friction and lubricity etc. Powder suppliers often develop customized alloys on demand with application-specific formulations.
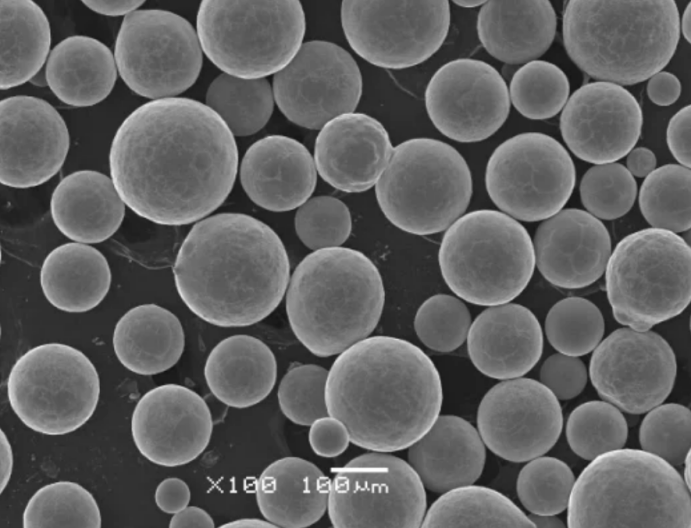

Characteristics of Copper Alloy Powder
Copper alloys display an attractive combination of physical and chemical characteristics that lend them useful for industrial parts and components. Some noteworthy properties are:
| Property | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Strength | Copper alloys like brasses and bronzes can achieve tensile strengths exceeding 1200 MPa, much greater than pure copper |
| Conductivity | Electrical and thermal conductivities lower than pure copper but considerably higher than ferrous alternatives |
| Corrosion resistance | Excellent corrosion resistance in range of environments from moisture, acids etc. through passivation |
| Machinability | Free machining copper alloys like leaded bronze easier to machine than steel; chip breakability improved |
| Wear resistance | Special compositions like copper-cobalt and copper-chromium developed for wear parts with hardness ~ 150 BHN |
| Coefficient of friction | Friction coefficient ranges from 0.2 for lubricated alloys to 1.0 for high friction materials tailored for specific uses |
| Permeability | Relative magnetic permeabilities from 10 to 10000 times that of austenitic stainless steel depending on alloy |
The diversity in achievable material characteristics makes copper alloys suitable for contacts, lead frames, bushings, welding tips, vacuum and high temperature uses etc. in addition to structural parts.
Applications of Copper Alloy Powder
The unique combination of conductivity, corrosion resistance, friction properties, machinability etc. shown by different copper alloys allows their use across an extensive range of industrial spheres:
| Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
| Automotive | Bushings, washers, welding tips, connectors, fasteners, switches, relays |
| Electrical | Contact strips, terminals, connectors, lead frames, fuses, resistor elements |
| Electronics | Lead frames, connectors, thermal management parts like heat sinks and heat spreaders |
| Engineering | Bearings, bushings, gears, wear parts |
| Industrial machinery | Bushings, plunger tips, valve parts, powder/toner application components |
| Medical and dental | Implants for pins, screws and plates due to biocompatibility |
| Military and defense | Firing pins, ammunition casings, bullet jackets |
| Oil and gas | Valves, pumps, submarine and downhole components |
The combination of strength, ductility, wear performance and intricate geometries possible make copper alloys suitable for small, medium and large structural parts across diverse industries.
Specifications of Copper Alloy Powder
Copper alloy powders are produced according to a range of international and regional specifications that define characteristics like composition limits, powder sizes and particle distributions, apparent density values, tap density values etc. Some key standards include:
| Standard | Grades | Elements limited |
|---|---|---|
| EN ISO 3522 | CuP2, CuP3, CuP4 etc. | Pb, As, Cd, Ni etc. |
| ASTM B177 | CDA Gilding Metal, Bronze CDA 854, C97300 etc. | S, Se, Te, Sb etc. |
| DIN 8513 | MF-CuSn8, MF-CuSn12, MFCuCr1 etc. | S, P etc. |
| GB/T 4337 | HB61, HB62, HB63 etc. | Zn, Ni, Al etc. |
| AWS A5.7 | ERCuNi, ERCuZn-C etc. | S, P, O etc. |
These define the standards for quality, consistency and reliability for sourcing powders. The permissible limits help control potentially detrimental impurities.
Copper Alloy Powder Sizes
Finer copper alloy powders below 100 microns facilitate higher densification during sintering to maximize mechanical properties in the final parts. They also enable better surface finish and feature detail. But handling becomes difficult. Coarser particles above 150 microns reduce dust issues but have lower sintered density. Hence a practical range is:
| Parameter | Typical size range |
|---|---|
| Maximum particle size | 150 μm |
| Minimum particle size | 15-20 μm |
| Average particle size | 45-75 μm |
Copper Alloy Powder Grades
Based on composition and powder characteristics, copper alloy powders are classified into grade groups like:
| Grades | Compositions | Common applications |
|---|---|---|
| Free machining | Leaded brasses and bronzes like Cu-Zn-Pb, Cu-Sn-Pb | Turned parts needing chip control |
| High conductivity | Cu-Ni, Cu-Fe | Electronics – leadframes, connectors etc. |
| Wear resistance | Cu-Cr, Cu-Co | Bearings, bushings, plungers |
| Strength | Complex Cu alloys like Cu-Ni-Si-Cr | High strength structural parts |
Production Process of Copper Alloy Powder
The popular techniques for production of copper alloy powders for industrial uses include:
- Atomization: Molten metal stream broken into fine droplets that solidify rapidly into powders
- Electrolysis: Electrochemical production where alloy components are co-deposited layer by layer
- Carbonyl process: Thermal decomposition of metal carbonyl vapors to produce fine particles
The benefits of these methods are ultrafine, spherical/irregular morphology powders with precise chemistry. Ready-to-press blends with lubricants can also be supplied as feedstock for shaping processes. The high purity, density and flowability of these powders result in high quality sintered components.
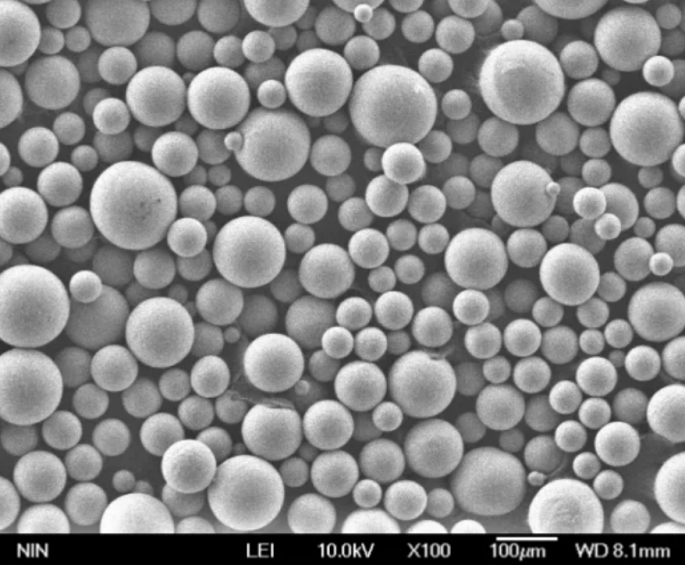

Suppliers of Copper Alloy Powder
Some of leading global producers of copper and alloy powders are:
| Company | Brands | Production capacity |
|---|---|---|
| Hoganas | Hoganas | 200,000 tons |
| GKN Hoeganaes | Hoeganaes, North American Höganäs | 180,000 tons |
| Makin Metal Powders | Makin | 20,000 tons |
| CNPC Powder Group | CNPC | 100,000 tons |
These companies have alloy design capabilities to tailor materials on demand and production capacities to supply small R&D volumes to large commercial quantities.
Pricing of Copper Alloy Powders
Prices vary based on:
| Parameter | Effect on pricing |
|---|---|
| Compositions | More expensive as alloying elements like Cr, Be, Co increase |
| Powder purity/quality | High purity medical/dental grades most costly |
| Order quantity | Larger quantity discounts available |
| Regional demand | Asia prices can be 30% lower than Europe/USA |
Typical price ranges are:
| Alloy Type | Price Range |
|---|---|
| Brass powders | $15-25 per kg |
| Bronze powders | $25-45 per kg |
| Copper-nickel-chromium | $50+ per kg |
Pricing also depends on additional services like particle size classification, ready-to-press mixing, and special packing that providers can offer.
Comparison of Copper Alloy Powders
A side-by-side analysis of different copper alloys reveals:
| Brass | Bronze | Copper-iron | Copper-nickel | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | Moderate | High | High | Moderate |
| Conductivity | High | Moderate | Very high | High |
| Corrosion resistance | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Very high |
| Wear resistance | Moderate | Low | Low | Moderate |
| Cost | Low | Moderate | Moderate | High |
So the appropriate copper alloy can be selected based on critical performance requirements.
Advantages of Copper Alloy Powders
Some useful benefits over bulk alloys are:
- Uniformity: No microsegregation and homogeneous microstructure
- Isotropic properties: Unlike cast products with anisotropy
- Fine grains: Rapid cooling results in very fine grains enhancing strength
- Workability: Easy formability into intricate, dense shapes
- Customization: Tailorable chemistry, particle size distribution as needed
- Productivity: Automated, high volume production with minimal scrap losses
- Quality: Consistency from batch-to-batch exceeds cast item variability
Limitations of Copper Alloy Powders
Some drawbacks are:
- Higher cost than bulk alloys
- Limited sizes and shapes compared to other forms
- Lower thermal and electrical conductivities after compacting
- May need protective atmosphere during sintering
- Possibility of grain growth if improperly sintered
- Special handling and containers needed to prevent oxidation