Table of Contents
Toggle1. Introduction
Stainless steel powder is a highly versatile material that finds extensive use in various industries due to its exceptional properties and durability. It is a finely divided form of stainless steel, consisting of small particles that can be shaped, molded, or blended with other materials to create unique products. This article explores the properties, applications, manufacturing process, and future trends of stainless steel powder.
2. What is Stainless Steel Powder?
Stainless steel powder is a powdered form of stainless steel, a corrosion-resistant alloy containing iron, chromium, nickel, and other elements. The powder is produced by atomizing molten stainless steel or by mechanically grinding larger pieces of stainless steel. The resulting powder particles are typically spherical or irregular in shape, with a size range from micrometers to millimeters.

3. Properties of Stainless Steel Powder
Stainless steel powder possesses several notable properties that make it highly desirable in various applications:
1. Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steel powder exhibits excellent resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for applications in aggressive environments. It forms a passive oxide layer on its surface, protecting it from rust, oxidation, and chemical degradation.
2. Mechanical Strength
Stainless steel powder retains the mechanical strength and toughness of solid stainless steel. It offers high tensile strength, hardness, and impact resistance, making it suitable for structural applications.
3. Heat Resistance
Stainless steel powder can withstand high temperatures without significant deformation or loss of properties. This heat resistance makes it suitable for applications in demanding thermal environments, such as aerospace and automotive industries.
4. Versatility
Stainless steel powder is a versatile material that can be tailored to specific applications. It can be alloyed with other elements to enhance certain properties or mixed with binders to form metal injection molding (MIM) feedstock for complex shapes.

4. Applications of Stainless Steel Powder
The unique properties of stainless steel powder enable its use in a wide range of applications across various industries:
1. Additive Manufacturing
Stainless steel powder is widely utilized in additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing. It allows the production of complex geometries and customized parts with high precision and mechanical integrity.
2. Metal Injection Molding (MIM)
Stainless steel powder, when mixed with binders, can be processed using the metal injection molding technique. MIM enables the production of intricate and net-shaped components used in industries like medical, automotive, and electronics.
3. Surface Coatings
Stainless steel powder is used in the production of corrosion-resistant coatings. These coatings are applied to various surfaces, such as automotive parts, kitchen appliances, and architectural structures, to enhance durability and aesthetics.
4. Powder Metallurgy
Stainless steel powder is a crucial component in the field of powder metallurgy. It is compacted and sintered to produce components like gears, bearings, and filters, offering high strength and wear resistance.
5. Chemical Industry
Stainless steel powder finds applications in the chemical industry due to its corrosion resistance. It is used for manufacturing storage tanks, pipes, valves, and fittings that come into contact with aggressive chemicals.

5. Manufacturing Process of Stainless Steel Powder
The production of stainless steel powder involves several key steps:
1. Atomization
Atomization is the most common method for producing stainless steel powder. Molten stainless steel is sprayed with a high-pressure gas or water jet, resulting in the breakup of the molten metal into fine droplets. These droplets solidify in flight and form powder particles.
2. Mechanical Grinding
Mechanical grinding is an alternative method for producing stainless steel powder. It involves the grinding of larger stainless steel pieces using specialized equipment, such as ball mills or vibratory mills, to break them down into fine powder particles.
3. Size Classification
After the production process, stainless steel powder undergoes size classification to ensure consistency and control over the particle size distribution. Various techniques like sieving, sedimentation, or air classification are employed for this purpose.
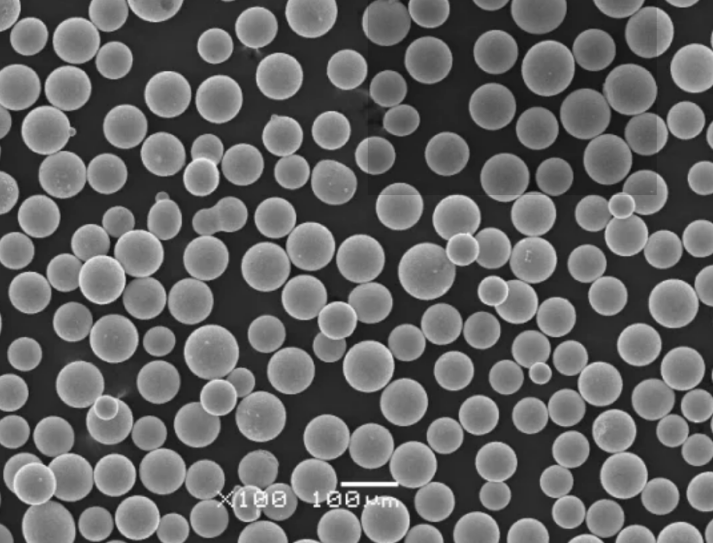
6. Types of Stainless Steel Powder
Stainless steel powder is available in different grades and compositions to suit specific applications. The most common types include:
1. Austenitic Stainless Steel Powder
Austenitic stainless steel powder contains high levels of nickel and chromium, offering excellent corrosion resistance and good formability. It is commonly used in the production of complex-shaped components.
2. Ferritic Stainless Steel Powder
Ferritic stainless steel powder has a higher iron content and lower nickel content compared to austenitic stainless steel. It exhibits good resistance to stress corrosion cracking and is often employed in automotive exhaust systems and architectural applications.
3. Martensitic Stainless Steel Powder
Martensitic stainless steel powder is characterized by its high strength, hardness, and wear resistance. It is frequently used in applications requiring components with excellent mechanical properties, such as cutting tools and turbine blades.
4. Duplex Stainless Steel Powder
Duplex stainless steel powder consists of a balanced mixture of austenitic and ferritic stainless steels. It offers a combination of high strength and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for applications in marine environments and oil and gas industries.
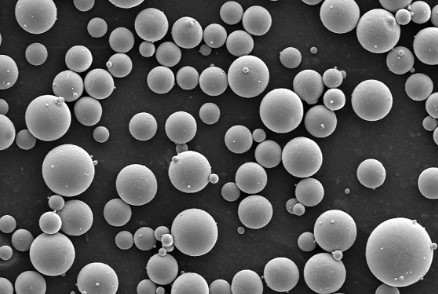
7. Advantages of Using Stainless Steel Powder
The utilization of stainless steel powder offers several advantages:
1. Design Freedom
Stainless steel powder enables the production of complex shapes and intricate geometries that are difficult to achieve using traditional manufacturing methods. It provides design freedom and flexibility for engineers and designers.
2. Cost Efficiency
By utilizing stainless steel powder, manufacturers can reduce material waste and achieve higher material utilization rates. Additionally, processes like additive manufacturing and metal injection molding can lower production costs by eliminating the need for extensive machining.
3. Enhanced Performance
Stainless steel powder imparts superior mechanical properties to components, such as high strength, hardness, and wear resistance. This enhanced performance makes it suitable for demanding applications where durability and reliability are crucial.
4. Customization and Tailoring
Stainless steel powder can be alloyed with other elements to modify its properties. This allows manufacturers to customize the material according to specific requirements, ensuring optimal performance in diverse applications.

8. Challenges in Working with Stainless Steel Powder
While stainless steel powder offers numerous benefits, there are certain challenges associated with its handling and processing:
1. Oxidation Susceptibility
Stainless steel powder is prone to oxidation when exposed to air or moisture. Care must be taken to store and handle the powder in an oxygen-free or controlled environment to prevent contamination and degradation.
2. Fire and Explosion Risks
Fine stainless steel powder particles can form explosive mixtures when dispersed in the air in specific concentrations. Adequate precautions, such as dust collection systems, grounding equipment, and explosion-proof facilities, must be implemented to mitigate these risks.
3. Powder Flowability
The flowability of stainless steel powder can vary depending on its particle size, shape, and surface properties. Poor flowability can lead to challenges in powder handling and processing, such as clogging, uneven distribution, or difficulties in achieving consistent fillings. It is crucial to optimize the powder’s flow characteristics to ensure smooth operations.
4. Contamination Control
Stainless steel powder is highly sensitive to contamination, as even small impurities can affect its properties and performance. Strict cleanliness measures should be implemented throughout the production process to avoid contamination from foreign particles or other metallic materials.
5. Health and Safety Considerations
When working with stainless steel powder, it is essential to consider health and safety precautions. Fine powder particles can pose respiratory hazards if inhaled, and skin contact should be minimized to prevent any potential irritation or sensitization. Adequate ventilation, personal protective equipment, and safe handling practices are necessary to ensure a safe working environment.

9. Safety Considerations when Handling Stainless Steel Powder
Working with stainless steel powder requires adherence to specific safety measures to mitigate risks and ensure the well-being of workers. Here are some important safety considerations:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Provide appropriate PPE, including gloves, safety glasses, dust masks or respirators, and protective clothing, to minimize the risk of exposure to powder particles and potential hazards.
- Ventilation and Dust Control: Maintain a well-ventilated workspace to prevent the accumulation of airborne particles. Use local exhaust systems and dust collection equipment to minimize dust levels and maintain air quality.
- Handling and Storage: Handle stainless steel powder with care, avoiding excessive agitation or dispersal. Store the powder in a dry, controlled environment to prevent moisture absorption and minimize the risk of oxidation.
- Fire and Explosion Prevention: Implement fire prevention measures, such as grounding equipment, static control, and appropriate storage containers. Avoid the formation of dust clouds and maintain a clean and organized workspace.
- Training and Education: Ensure that workers receive proper training on the safe handling and storage of stainless steel powder. Educate them about potential hazards, emergency procedures, and the correct use of personal protective equipment.
10. Future Trends in Stainless Steel Powder Technology
The field of stainless steel powder technology continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements and industry demands. Here are some future trends to watch for:
1. Improved Powder Quality Control
Manufacturers are investing in advanced quality control techniques to ensure consistent and high-quality stainless steel powder. Innovations in particle size analysis, shape characterization, and chemical composition analysis contribute to enhanced powder performance and process reliability.
2. Alloy Development and Tailoring
Research and development efforts focus on expanding the range of stainless steel powder alloys to meet specific application requirements. By incorporating new alloying elements or optimizing existing compositions, manufacturers can tailor the material’s properties for enhanced performance and versatility.
3. Sustainable Production and Recycling
As sustainability becomes a key concern, efforts are underway to develop environmentally friendly production processes for stainless steel powder. Recycling and reuse strategies are being explored to minimize waste and promote circular economy practices in the powder metallurgy industry.
4. Integration with Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
The integration of stainless steel powder with advanced manufacturing technologies like additive manufacturing, metal injection molding, and selective laser melting continues to expand. This convergence enables the production of complex, lightweight, and highly functional components with improved efficiency and reduced material waste.
5. Surface Modification and Coating Innovations
Researchers are exploring novel surface modification techniques and coatings to enhance the performance and durability of stainless steel powder components. Surface treatments like plasma nitriding, physical vapor deposition, or nanocoating technologies offer improved wear resistance, reduced friction, and enhanced corrosion protection.
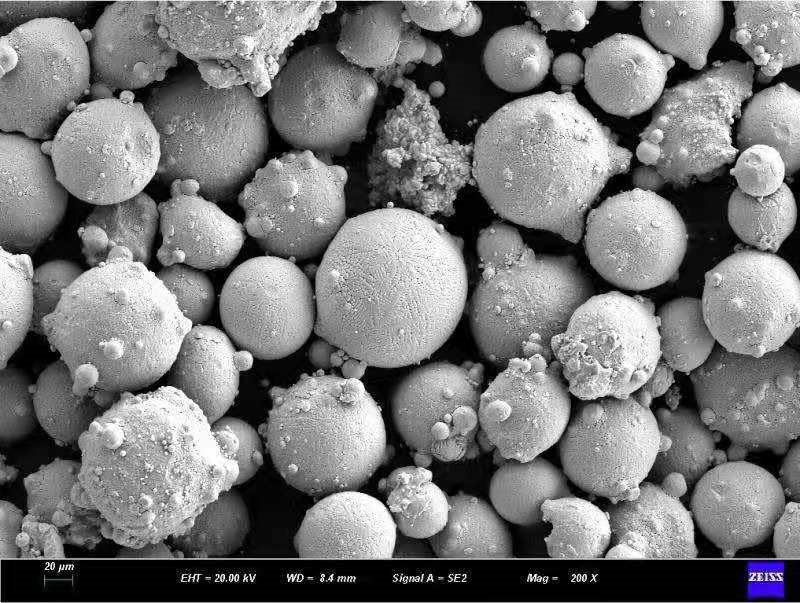

11. Conclusion
Stainless steel powder is a versatile material with a wide range of applications across various industries. Its corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and heat resistance make it an ideal choice for demanding environments. By leveraging its unique properties, manufacturers can produce complex components, coatings, and structures that meet specific requirements. However, working with stainless steel powder requires attention to safety considerations due to its potential health hazards and safety risks. As technology advances, the future of stainless steel powder holds promise in terms of improved quality control, sustainable production, and integration with advanced manufacturing techniques.
FAQs
Q1: Can stainless steel powder be recycled? Yes, stainless steel powder can be recycled through various processes. Recycling methods include reclaiming excess powder, reusing powder from failed prints, or implementing closed-loop recycling systems within the manufacturing process.
Q2: Is stainless steel powder suitable for food-grade applications? Yes, certain grades of stainless steel powder, such as austenitic stainless steel, are commonly used in food-grade applications. These grades offer excellent corrosion resistance and are safe for contact with food and beverages.
Q3: What are the key differences between stainless steel powder and solid stainless steel? Stainless steel powder and solid stainless steel share similar properties but differ in their form and processing methods. Stainless steel powder is finely divided and used in powder metallurgy processes, while solid stainless steel is in the form of solid sheets, bars, or components.
Q4: Can stainless steel powder be used in outdoor applications? Yes, stainless steel powder is well-suited for outdoor applications due to its corrosion resistance. It is commonly used in architectural structures, outdoor equipment, and automotive components exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Q5: What safety precautions should be taken when handling stainless steel powder? When working with stainless steel powder, it is important to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), maintain good ventilation, and prevent dust accumulation. Adhering to proper handling and storage practices minimizes the risk of respiratory and skin hazards.