Tabla de contenidos
ToggleTungsten carbide (WC) is an extremely hard, heat and wear resistant material made by mixing tungsten powder and carbon powder in a process called carburization. Tungsten carbide is one of the most important carbides and the most widely used in industrial and commercial applications.
Overview of Tungsten Carbide Powder
Tungsten carbide powder, also known as cemented carbide, is a composite material manufactured by mixing tungsten powder and carbon powder followed by sintering compacted powder blend in a protective atmosphere at temperatures of 1400-1500°C.
The resulting tungsten carbide material is characterized by exceptional hardness, wear resistance, strength, and toughness properties making WC an ideal material for cutting tools, mining and drilling where it frequently outperforms steel and where high stresses are encountered together with wear.
Tungsten carbide powders are produced in different grades of particle sizes, shapes, surface area and chemistries for use in diverse powder metallurgy, thermal spray, welding and hardmetal/cemented carbide applications across industry.
Tungsten Carbide Powder Types
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Macro grain WC powder | For heavy machining applications requiring good wear resistance. Particle size > 1 micron |
| Micro grain WC powder | Widely used for toughness in mining tools and drill bits. Particle size 1-0.5 microns |
| Ultrafine grain WC powder | High hardness applications like cutting tools, die inserts. Particle size < 0.5 microns |
| Nanometer WC powder | Specialist applications demanding maximum abrasion resistance. Particle size under 100 nm |
Composition of Tungsten Carbide Powder
Tungsten carbide is composed of atoms of tungsten (W) and carbon (C) in a one to one ratio. It has the chemical formula WC, and a molecular weight of 195.86 g/mol.
The composition and structure of cemented carbides can be varied to optimize properties for different applications. Small amounts of other carbides or metals are frequently added. Some common additives are listed below:
| Additive | Function | Typical Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Cobalt | Binder metal | 3 – 25 wt% |
| Titanium carbide | Grain growth inhibitor | 0 – 8% |
| Tantalum carbide | Thermal shock resistance | 0 – 8% |
| Niobium carbide | Wear resistance | 0 – 8% |
Properties of Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide possesses substantially superior properties compared to high speed steel and make it ideal for applications requiring high wear resistance.
Some key properties are outlined below:
| Property | Tungsten Carbide Value |
|---|---|
| Density | 14.95 g/cm<sup>3</sup> |
| Melting point | 2870°C |
| Hardness | 88 – 93 HRA |
| Compressive strength | 5.52 GPa |
| Fracture toughness | 10 – 15 MPa√m |
The exceptional hardness, wear resistance, strength and thermal properties allow it to outperform steel in challenging mechanical, mining, machining and drilling applications.
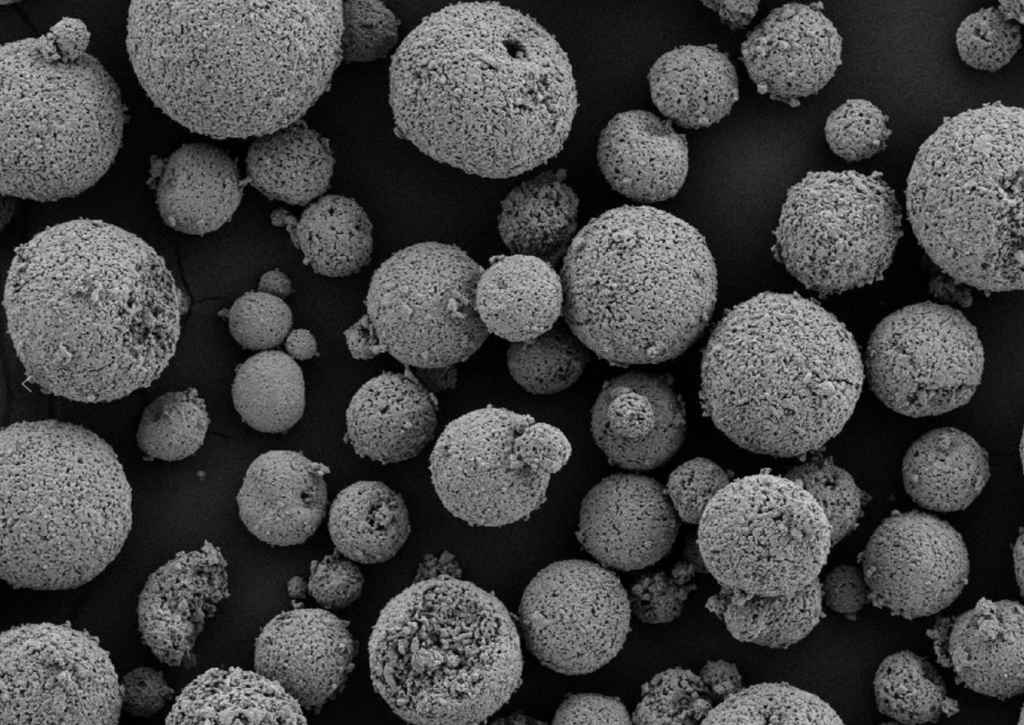

Characteristics of Tungsten Carbide Powder
The characteristics and quality metrics used to assess tungsten carbide powders are shown in the table below:
| Characteristic | Typical Specification | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon content | Typically 6.09 – 6.13 wt% | Carbon provides the hardness |
| Oxygen content | < 0.5 wt% | High oxygen can reduce hardness |
| Total impurities | < 0.4 wt% | Impurities reduce density and hardness |
| Particle size | 0.2 to 15 microns | Submicron sizes enhance properties |
| Specific surface area | 0.4 to 5 m<sup>2</sup>/g | Higher values promote sintering |
| Morphology | Angular, rounded | Rounded/spherical powders have better flowability |
Controlling powder characteristics like particle size distribution, purity levels, surface area, morphology and microstructure is essential for achieving dense compacts and consistent product quality after sintering.
Applications of Tungsten Carbide
The unique properties of extreme hardness, wear resistance, high strength, and thermal shock resistance lend tungsten carbide to be extremely widely used across applications including:
Tungsten Carbide Applications
| Industry | Examples of WC Applications |
|---|---|
| Mining | Drill bits, drag bits, impregnated diamond bits |
| Machining | Cutting tools, inserts, end mills |
| Construction | Masonry drills, saw tips, earth boring tools |
| Manufacturing | Extrusion dies, forming tools, pelletizer knives |
| Automotive | Fuel injection nozzle tips, brake pad abrasives |
| Electronics | Circuit board drills, wire drawing dies |
Tungsten carbide maintains its hardness at elevated temperatures far better than other abrasion resistant materials. This allows it to cover an exceptionally wide range of applications across industry.
Tungsten Carbide Powder Specifications
Tungsten carbide powder is produced in a range of particle size distributions, purity levels, surface area specifications, oxide levels and morphology grades to meet application needs:
| Specification | Typical Range | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | 0.2 to 15 microns | Submicron for best properties. Match to application |
| Carbon content | 6.09 – 6.13 wt% | Essential for mechanical properties |
| Total impurities | < 0.4 wt% | High purity prevents defects |
| Specific surface area | 0.4 to 5 m<sup>2</sup>/g | Higher values promote sintering |
| Oxide (O2) level | < 0.5 wt% | Oxides reduce hardness and fracture resistance |
| Cobalt | 3 – 25 wt% | Binder phase. Varies to optimize strength, hardness and/or toughness |
| Grain growth inhibitors | Titanium carbide, tantalum carbide etc | Help control microstructure |
International standard test methods like ISO 4499 are used for analysis and testing of cemented carbide powders. Common methods are wet analysis, XRD, particle size analysis using laser diffraction techniques.
Grades of Tungsten Carbide Powder
Tungsten carbide is categorized into grades based on properties, manufacturing method, quality level, end use or other specifications:
| Grade | Description | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Micrograin WC | 0.5-1 micron powder | Toughness for mining, construction tools |
| Ultra fine grade WC | Micron to submicron powder | Hardness for cutting inserts, dies |
| Rotating bending strength | Classified by transverse rupture strength | Mining and construction applications |
| Wear resistance grade | Related to abrasion resistance | Wear parts, dies, cutting inserts |
| Chemical vapor deposited (CVD) coated | Uniform pure WC coating 1-50 microns thick | High performance wear parts |
International standards help define tungsten carbide grades for composition, properties, manufacture and testing including ISO 513 and ASTM B776.
Global Standards for Tungsten Carbide Powder
The widely accepted global standards for composition, testing, analysis and classification of tungsten carbide powders are shown below:
Global Tungsten Carbide Standards
| Standard # | Standard Title |
|---|---|
| ISO 513 | Cemented carbides – Determination of transverse rupture strength |
| ISO 3326 | Cemented carbides — Determination of oxygen content by fusion — Infrared detection method |
| ISO 4499 | Cemented carbides – Determination of carbon content – Infrared detection method after combustion in an induction furnace |
| ASTM B388 | Standard Specification for Thermomechanical Controlled Billets of Tungsten-Copper Composite Rod |
| ASTM B776 | Standard Specification for Hafnium Powder and Hafnium Alloy Powder |
These global standards for material composition, testing procedures, sampling, analysis and specifications facilitate quality control and technical understanding between international manufacturers, distributors and end users.
Suppliers of Tungsten Carbide Powder
Tungsten carbide powder is commercially manufactured by several leading suppliers globally. Some major WC powder producers include:
| Company | Headquarters Location |
|---|---|
| Sandvik | Stockholm, Sweden |
| Kennametal | Latrobe, PA, USA |
| Guangdong Xianglu Tungsten | Ganzhou City, China |
| Japan New Metal (JNMET) | Nagoya, Japan |
| Wolfram Company | Schwäbisch Gmünd, Germany |
Consumers can procure tungsten carbide powders directly from producers or through several specialty distributors and resellers globally. When selecting a WC grade, consider factors like application requirements, price point, lead times, certifications, and prior supplier relationship.
Pricing for Tungsten Carbide Powder
Tungsten carbide pricing depends on several parameters like particle size, carbon content, morphology, surface area and purchase quantity. Some typical tungsten carbide powder costs are shown below:
| Type | Price Range |
|---|---|
| Micrograin WC powder | $27 – $45 per lb |
| Nanoscale WC powder | $160 – $240 per lb |
| Rotating bending strength grade | ~$33 per lb |
| Chemical vapor deposited WC | $80+ per lb |
Pricing also depends on distribution channel – buying directly from a manufacturer provides lower pricing compared to purchasing from a reseller or distributor. Larger purchase volumes also enable negotiated supplier discounts in most cases.
Comparison of Tungsten Carbide to Other Hard Materials
Tungsten carbide has exceptionally high hardness and wear performance compared to other industrially important materials:
| Material | Hardness (Vickers) | Wear Resistance | Fracture Toughness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tungsten carbide | 2500-3500 HV | Excellent | Moderate 10-15 MPa√m |
| Titanium nitride | 2000-2200 HV | Very good | Low at ~6 MPa√m |
| Alumina ceramics | 1800-2200 HV | Good | Low to moderate |
| Tool steel | 650-850 HV | Moderate | Higher than WC |
| Stainless steel | 150-300 HV | Low | Excellent |
Among all commonly used materials, cemented carbide possesses the best combination of hardness, wear performance and fracture toughness – enabling it to cover the broadest range of demanding industrial applications.
Advantages of Using Tungsten Carbide Powder
Utilizing tungsten carbide provides significant benefits including:
- Extremely high hardness – allows outstanding wear performance in mining, machining etc
- Strength and fracture toughness superior to ceramics
- Maintains hardness at high temperatures – stays rigid at 800°C
- Resists corrosion in acidic/alkaline environments
- High thermal conductivity aids heat dissipation from cutting edges
- Range of material grades available to optimize properties
The unique performance properties of tungsten carbide powders make it a critically enabling material across production engineering.
Limitations of Tungsten Carbide Powder
Despite the advantages, tungsten carbide use also has certain restrictions:
- Brittle failure – Sudden cracking under high loads due to low strain tolerance
- High materials costs – Tungsten is relatively rare and WC manufacturing requires extensive processing
- Low thermal shock resistance – Risk of cracking when subjected to sudden high temperatures
- Limited chemical resistance – Dissolves in highly alkaline hot sodium hydroxide solutions
- Difficult recycling – Reclaiming tunsgten scrap has low yields
By understanding limitations relating to brittleness, cost or environmental stability, end-users can make informed selections of appropriate tungsten carbide grade for their specific application requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
FAQs about Tungsten Carbide Powder
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is tungsten carbide powder made of? | Tungsten carbide powder is made by mixing pure tungsten powder and carbon powder in a ball mill. Powder is milled together with an organic wax binder and pressed into a compact before sintering at 1500°C in hydrogen to form WC. |
| Why is tungsten carbide so hard? | Extreme hardness results from unique interatomic bonding where carbon atoms fit into interstices between tungsten atoms – forming an incredibly hard and stable crystal lattice structure. |
| What is the difference between tungsten and tungsten carbide? | Tungsten is a pure metal with density of 19 g/cm3 while tungsten carbide is a composite made with tungsten and carbon atoms. Tungsten itself is relatively soft while WC is amongst the hardest materials known. |
| How strong is tungsten carbide? | Tungsten carbide has extremely high hardness at 2500-3500 Vickers, compressive strength over 5 GPa and flexural strength ~2-3 GPa – much higher than almost any steel. |
| Is tungsten carbide brittle? | Tungsten carbide grades have relatively low fracture toughness and strain tolerance, making them susceptible to sudden brittle cracking under high loads beyond material strength limits. Proper design is essential to avoid this. |
| Is tungsten carbide expensive? | Tungsten carbide costs significantly more than tool steel due to extensive processing of tungsten ores but matches performance justify higher prices for wear critical applications like cutting inserts. |