Table of Contents
ToggleNiobium powder in spherical morphology offers unique benefits for various applications requiring a combination of high strength, corrosion resistance, superconductivity, and other specialized properties. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of spherical niobium powder covering composition, properties, manufacturing, grades, specifications, applications, pricing, suppliers, pros/cons, and other details.
Overview of Spherical Niobium Powder
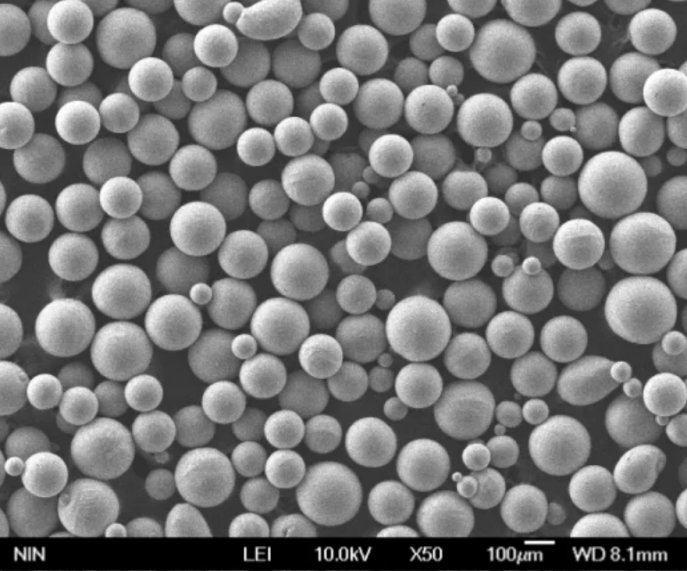
Spherical niobium powder consists of small near-perfect spherical particles composed of niobium metal with a typical purity above 99%. The spherical shape improves flow and packing density compared to angular powder.
Key properties that make spherical niobium powder useful include:
- High strength and modulus
- Excellent corrosion resistance
- Low coefficient of friction
- Superconductivity at low temperatures
- Thermal shock resistance
- Biocompatibility and non-toxicity
Fine spherical niobium powder is used in thermal spray coatings, capacitors, superconductors, additive manufacturing, biomedical implants and other advanced applications. This guide covers composition, properties, manufacturing, specifications, grades, and applications of spherical niobium powder products.

Composition of Spherical Niobium Powder
Niobium, also known as columbium, is a refractory transition metal with atomic number 41. Commercial niobium powder typically has the following impurity limits:
| Element | Composition by Weight |
|---|---|
| Niobium (Nb) | 99.8% minimum |
| Oxygen (O) | 2000 ppm max |
| Nitrogen (N) | 100 ppm max |
| Carbon (C) | 500 ppm max |
| Hydrogen (H) | 100 ppm max |
| Iron (Fe) | 200 ppm max |
| Tantalum (Ta) | 1000 ppm max |
| Tungsten (W) | 100 ppm max |
High purity is required for many niobium applications. More stringent grades have purity of 99.99% or higher. Oxygen and nitrogen are controlled since they can embrittle niobium.
Properties of Spherical Niobium Powder
Key properties of spherical niobium powder include:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Density | 8.57 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 2468°C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 53.7 W/m-K (at 20°C) |
| Electrical Resistivity | 12.4-14 μΩ-cm (at 20°C) |
| Young’s Modulus | 105 GPa |
| Tensile Strength | 200-400 MPa |
| Elongation | 20-45% |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent resistance to many acids and oxidizing media |
| Superconducting Temperature | 9.2 K |
The properties make it suitable for uses needing strength, conductivity, and corrosion resistance.
Manufacturing Process of Spherical Niobium Powder
Spherical niobium powder is produced using gas atomization, an advanced powder metallurgy process with the following steps:
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Melting | High purity niobium is induction melted in a vacuum or inert gas |
| Atomization | The melt stream is atomized with an inert gas into fine droplets |
| Solidification | The droplets rapidly solidify into spherical powder particles as they cool |
| Collection | The spherical powder is collected in a chamber below the nozzle |
| Screening | Particles are sieved to the desired size ranges |
Atomization parameters are controlled to achieve the particle size distribution, flow characteristics, apparent density, and purity required. The inert gas prevents oxidation.
Sizes and Size Distribution of Spherical Niobium Powder
Spherical niobium powders are available in various size distributions categorized by standard mesh sizes:
| Mesh Size | Particle Size (μm) |
|---|---|
| -325 | Less than 44 |
| -230 | 44-63 |
| -170 | 63-90 |
| -140 | 90-125 |
| -100 | 125-149 |
| -325+500 | 15-44 |
| -230+270 | 63-74 |
Typical size distributions maintain a coefficient of variation under 30% for consistent particle sizes. Smaller sizes below 10 μm can be produced with special atomization techniques.
Grades of Spherical Niobium Powder
Spherical niobium powder is available in a range of purity levels and specifications:
| Grade | Purity (%) | Oxygen (ppm) | Carbon (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade A | 99.8 | 1200 | 400 |
| Grade B | 99.9 | 800 | 300 |
| Grade C | 99.95 | 500 | 200 |
| Grade D | 99.99 | 100 | 50 |
Higher grades like Grade D offer enhanced purity and lower interstitial impurity levels required for specialty applications.
Applications of Spherical Niobium Powder
Key applications using spherical niobium powder include:
| Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
| Electronics | Multilayer ceramic capacitors, superconductor films |
| Coatings | Thermal spray coatings, surface enhancement |
| Chemical | Hydrogen storage, catalysts, batteries |
| Manufacturing | Metal injection molding, additive manufacturing |
| Medical | Implants, radiopaque markers |
| Aerospace | Rocket nozzles, combustion chambers |
The optimized particle shape improves packing density and performance in sintering, thermal spraying, printing, and composites manufacturing.
Global Suppliers of Spherical Niobium Powder
Some of the major global suppliers of spherical niobium powder include:
| Company | Location |
|---|---|
| H.C. Starck | Germany, US |
| CBMM | Brazil |
| Jien Nickel | China |
| Japan New Metals Co | Japan |
| Micron Metals | US |
| TaeguTec | South Korea |
Reputable manufacturers produce spherical niobium powder to high standards matching application requirements. Some offer additional services like thermal spray coatings.
Pricing of Spherical Niobium Powder
Spherical niobium powder costs range based on purity, particle size, distribution, quantity, and manufacturer:
- Purity: 99.8% grades – $50-80/lb, 99.9% grades – $60-100/lb, 99.99% grades – $150-300/lb
- Particle size: Prices increase for smaller sizes below 44 μm
- Quantity: Bulk discounts at order volumes above 25-50 lbs
- Manufacturer: Premiums for high end grades from top manufacturers
Contact established niobium suppliers for an exact price based on your specifications and quantity.

Pros and Cons of Spherical Niobium Powder
Advantages
- High strength and hardness
- Excellent corrosion resistance
- Low friction coefficient
- High thermal shock resistance
- Superconducting properties
- Biocompatible for medical uses
- Spherical shape improves packing and flow
Disadvantages
- High cost compared to other metals
- Brittle with low ductility when cold
- Requires inert processing due to reactivity
- Limited global supply and production
- Oxides negatively impact performance
- Difficult to machine in solid form
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between spherical and irregular niobium powder?
A: Spherical powder has a near-perfect rounded shape compared to angular or irregular powder. This improves flow, packing density, and performance in applications like thermal spraying.
Q: What particle size is best for thermal spray coatings?
A: For most thermal spray processes, sizes from -170 mesh to -325 mesh (44 to 125 μm) work well. Finer sizes below 10 μm can be used for suspension or solution precursor plasma spraying.
Q: Is niobium powder flammable or explosive?
A: Niobium powder is not flammable or explosive on its own but fine powders can form explosive dust clouds when dispersed. Inert gas processing is recommended.
Q: Is spherical niobium powder toxic?
A: Niobium metal has very low toxicity and is considered safe for human contact or implantable medical devices. Handling precautions are advised.
Q: How is spherical niobium powder stored and handled?
A: Inert gas sealing and dry storage is recommended. Tightly sealed containers prevent oxygen and moisture absorption which can degrade the powder properties.
Conclusion
With its optimized spherical morphology and purity, spherical niobium powder provides enhanced performance in electronics, coatings, manufacturing, chemical, biomedical and other critical applications.
When matched to specifications, spherical niobium powder delivers improved flow, packing density, strength, and conductivity needed for next-generation technologies and processes while maintaining niobium’s inherent corrosion resistance.