Table of Contents
ToggleImagine a material that can withstand scorching temperatures, resist relentless corrosion, and be shaped into intricate components. This is the reality of Nickel Based Powders, a class of finely ground metallic particles revolutionizing diverse industries.
Delving into the Compositional Landscape
Nickel forms the foundation of these powders, typically exceeding 99% purity. However, its true magic lies in the strategic addition of other elements, each playing a specific role:
Chromium: Enhances high-temperature resistance and oxidation defiance.
Molybdenum: Fortifies strength at elevated temperatures.
Aluminum and Titanium: Contribute to lightweight properties while maintaining strength.
Tantalum and Niobium: Further elevate high-temperature capabilities.
This careful alloying process unlocks a spectrum of properties, tailoring the powder to specific applications.

Applications of Nickel Based Powders
Nickel-based powders find themselves at the heart of various applications, each leveraging their unique properties:
Additive Manufacturing (AM):
Nickel-based powders are the building blocks of this innovative process. These fine, metallic particles, primarily composed of nickel and often combined with other elements, act as the “ink” in the AM “printer.” They are meticulously laid down, layer by painstaking layer, until the desired 3D object takes form. This transformative technology unlocks a world of possibilities, pushing the boundaries of what we can design and manufacture.
Let’s delve deeper into some of the remarkable applications of nickel-based powders in AM:
Conquering the Skies: Turbine Blades – In the heart of a jet engine, where temperatures soar and pressures reach unimaginable heights, nickel-based powders become the heroes. They are used to create turbine blades, the workhorses that convert the energy of hot gases into thrust, propelling airplanes forward. These blades need to be incredibly strong and resistant to extreme heat and pressure, and nickel-based powders deliver precisely those properties, making them the perfect material for this demanding application.
Healing and Innovation: Medical Implants – The human body is a complex and delicate system. When medical intervention is necessary, the materials used need to be biocompatible, meaning they can coexist with the body without causing harm. Nickel-based powders come to the rescue again, offering exceptional biocompatibility and outstanding durability. They are used to create medical implants, such as hip replacements and dental implants, that seamlessly integrate with the body, restoring function and improving quality of life.
Reaching for the Stars: Aerospace Components – In the relentless pursuit of lighter and stronger materials for aircraft, nickel-based powders play a crucial role. AM allows for the creation of intricate aerospace components with complex geometries, all while maintaining incredible strength-to-weight ratios. This translates to lighter, more fuel-efficient airplanes, pushing the boundaries of flight and exploration.
Thermal Spraying:
Thermal spraying is akin to painting with molten metal. Nickel-based powders are transformed into a stream of hot, tiny particles, which are then propelled at high velocity towards a target surface. Upon impact, these particles rapidly solidify, forming a thin, yet robust, metallic coating. This coating acts as a second skin, imbuing the object with enhanced properties, making it more resistant to:
Corrosion’s Corrosive Grip: Pipelines, valves, and other equipment exposed to harsh environments like seawater or chemicals are particularly susceptible to corrosion, a process that eats away at the metal. Nickel-based powders form coatings that are highly resistant to corrosion, effectively shielding the underlying material and extending its lifespan.
Wear and Tear’s Relentless Assault: Machinery and tools experience constant friction and wear, leading to their eventual breakdown. Nickel-based powders can be formulated to create wear-resistant coatings, significantly reducing friction and extending the life of components, leading to cost savings and reduced downtime.
Heat’s Unrelenting Grip: In applications like heat exchangers and other thermal management systems, efficient heat transfer is crucial. Nickel-based powders can be chosen specifically for their excellent thermal conductivity, ensuring optimal heat flow and preventing overheating, which can damage sensitive equipment.
Powder Metallurgy (PM):
Precise Filtration: High-Performance Filters – In the realm of chemical processing and filtration systems, precision is paramount. Nickel-based powders allow for the creation of high-performance filters with precisely controlled pore sizes and exceptional filtering efficiency. These filters can be tailored to capture specific contaminants, ensuring the purity and integrity of various products and processes.
Conducting with Confidence: Electrical Contacts – The smooth flow of electricity is vital in countless applications, from electronic devices to power grids. Nickel-based powders are instrumental in the creation of electrical contacts, the crucial components that connect circuits and ensure seamless current transfer. These contacts offer superior conductivity, ensuring minimal electrical loss, and boast remarkable wear resistance, guaranteeing reliable performance over extended periods.
Unrelenting Sharpness: Cutting Tools – The heart of any cutting operation lies in the tool’s ability to maintain a sharp edge. Nickel-based powders are used to manufacture cutting tools with exceptional hardness, allowing them to cut through tough materials with ease. Moreover, these powders can be formulated to retain their sharpness for extended periods, minimizing the need for frequent replacements and enhancing overall machining efficiency.

Understanding the Key Characteristics and Properties
The following table summarizes the key characteristics and properties of nickel-based powders:
| Characteristic/Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Composition | Primarily nickel, alloyed with elements like chromium, molybdenum, aluminum, titanium, tantalum, and niobium. |
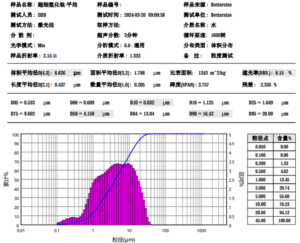
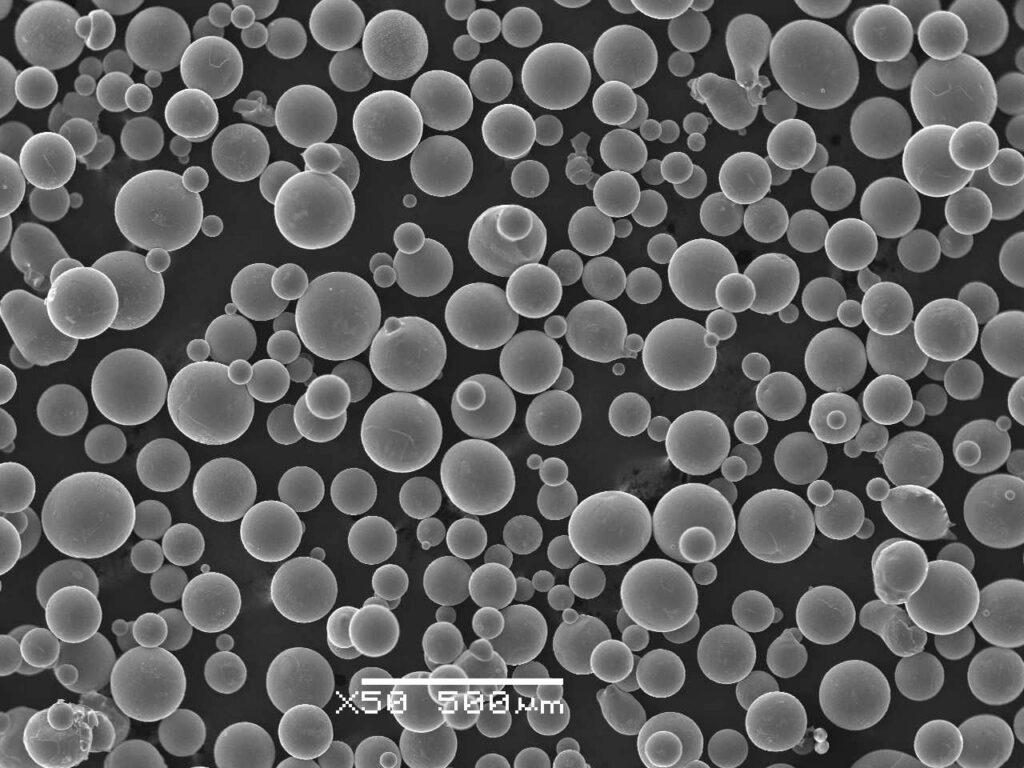
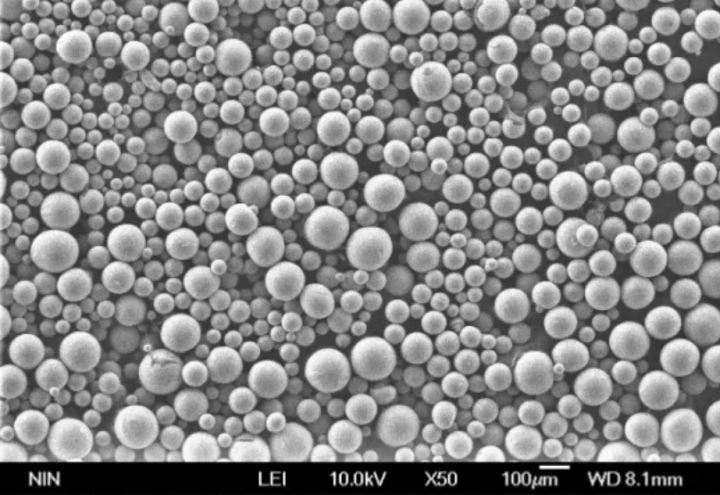
| Particle size and morphology | Typically range from 10 to 150 microns, with spherical or irregular shapes. |
| Density | Generally between 7.5 and 9 g/cm³, depending on the specific alloy composition. |
| Melting point | Varies based on the alloying elements, typically ranging from 1300°C to 1600°C. |
| High-temperature strength | Maintains strength and structural integrity at elevated temperatures. |
| Corrosion resistance | Excellent resistance to various corrosive environments, including oxidation, acids, and alkalis. |
| Wear resistance | Exhibits superior resistance to wear and tear, extending component lifespan. |
Navigating the World of Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards
The selection of the appropriate nickel-based powder is crucial for achieving optimal performance. Several factors need consideration:
Specifications:
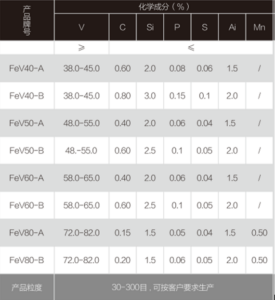
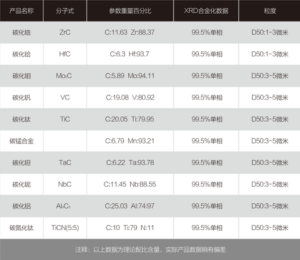
Chemical composition: Precise percentages of constituent elements to meet specific application requirements.
Particle size distribution: Influences the flowability, packing density, and final product properties.
Surface morphology: Affects powder behavior in various processing techniques.
Sizes and Grades:
Nickel-based powders are available in a range of sizes, typically between 10 and 150 microns, catering to diverse applications.
Different grades offer varying levels of purity and specific properties tailored to specific needs.
Standards:
Established standards like ASTM International (ASTM) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) ensure consistent quality and performance of nickel-based powders.
A Comparative Analysis: Weighing the Pros and Cons
While nickel-based powders offer numerous advantages, it’s essential to be aware of their limitations:
Advantages:
Exceptional high-temperature performance: Ideal for applications like turbines and heat exchangers.
Outstanding corrosion resistance: Protects against harsh environments, extending component life in demanding applications.
Enhanced wear resistance: Minimizes wear and tear, leading to improved product longevity and reduced maintenance costs.
Tailorable properties: Through various alloying combinations, nickel-based powders can be customized to meet specific application requirements.
Versatility: Applicable across diverse industries, from aerospace and energy to medicine and manufacturing.
Limitations:
Cost: Compared to some conventional materials, nickel-based powders can be more expensive due to their complex manufacturing processes and unique properties.
Health and safety considerations: Nickel dust can pose health risks if not handled appropriately during processing. Implementing proper safety protocols and adhering to recommended handling procedures is crucial.
Processing complexities: Utilizing nickel-based powders in certain techniques like AM might require specialized equipment and expertise, potentially increasing production costs and complexity.
FAQs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What are the different types of nickel-based powders? | The specific type of nickel-based powder is determined by its alloying elements and their proportions. Common types include Inconel, Invar, Monel, and Hastelloy, each with unique properties suited for specific applications. |
| How are nickel-based powders produced? | Various methods are employed, including carbonyl process, water atomization, and plasma atomization. Each method offers distinct advantages and limitations influencing the powder’s characteristics. |
| What are some emerging applications of nickel-based powders? | Research and development are ongoing, exploring applications in areas like battery technology, fuel cells, and lightweighting for sustainable transportation solutions. |
| Where can I find more information about nickel-based powders? | Reputable industry associations, academic research papers, and technical resources from trusted manufacturers can provide further details and insights. |
Conclusion
Nickel-based powders stand as a testament to material science advancements. Their exceptional properties have revolutionized various industries, enabling the creation of high-performance, durable, and innovative components. As research and development continue, we can expect even more exciting applications for these versatile materials in the future.