Tabla de contenidos
ToggleCopper alloy powder represents a versatile material for manufacturing and surface engineering across industries. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of various copper powder types, compositions, key characteristics, manufacturing methods, usage in coatings, pressing, injection molding, pricing, and supplier details.
What is Copper Alloy Powder?
Copper alloy powder consists of copper combined with other elements like zinc, tin, aluminum, nickel, silicon, chrome etc. at the microscopic particulate level. Blending balances material strengths like thermal/electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, wear protection, hardness, and tailors them to end-use case specifications.
Key properties that make copper alloy valuable:
- High thermal and electrical conductivity
- Corrosion resistance
- Impact and wear resistance
- Customizable mechanical properties
- Solderability
- Manufacturability via powder metallurgy
Adjustment of copper with secondary metals expands options beyond pure copper and brass powder across industries from automotive, marine, electronics, defense and more.
Copper Alloy Powder Composition
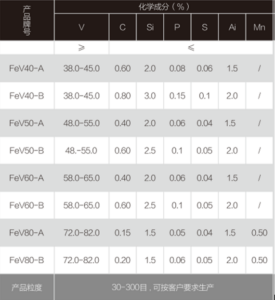
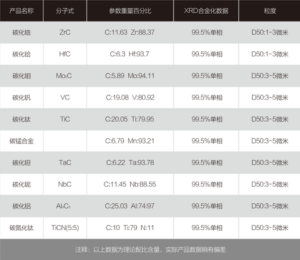
There exist thousands of potential combinations and ratios of copper alloys. Some common alloys and their elemental makeups are:
| Alloy Type | Major Components |
|---|---|
| Brass | Copper + Zinc |
| Bronze | Copper + Tin + Zinc |
| Copper-Nickel | Copper + Nickel |
| Cupronickel | Copper + Nickel + Manganese |
| Nordic Gold | Copper + Zinc + Aluminum + Tin |
Trace elements like iron, lead, phosphorus, graphite or magnesium may be present in certain alloys as well. Specifying purity levels filters out contaminants.
Alloy grades define percentages – for example CuZn30 signifies 70% copper, 30% zinc. Varying ratios tailor hardness, strength, melting points and conductivity as per application needs.
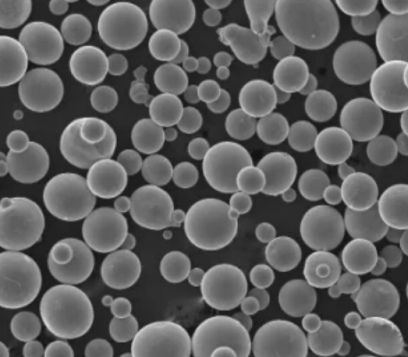
Key Properties of Copper Powder Alloys
Copper alloy particles demonstrate valued characteristics:
| Property | Contribution |
|---|---|
| Electrical conductivity | Efficient thermal dissipation prevents overheating |
| Thermal conductivity | Rapid heat transfer maintains operating temperatures |
| Corrosion resistance | Withstands weathering and atmospheric exposure |
| Antimicrobial qualities | Inherent biostatic surface activity reduces microbes |
| Noise dampening | Absorbs vibrations and sound energy |
| Machinability | Softer than ferrous alloys, easier to fabricate |
| Friction resistance | Maintains lubricity between sliding surfaces |
| Spark resistance | Mitigates ignition risk around combustibles |
Varying elemental ratios tunes properties like tensile strength, melting point, platability, and magnetism to meet application challenges from salty marine environments to high voltage circuits.
Copper Alloy Powder Manufacturing
Commercial production methods for copper alloy powder include:
| Method | Details | Particle Sizes |
|---|---|---|
| Atomization | Molten metal stream spun into tiny droplets that cool rapidly | 5μm to 150μm |
| Carbonyl | Chemical reaction deposits pure metal onto particles | 1μm to 15μm |
| Roller Mill | Compacting and grinding metal into flat flakes | 100 mesh flakes (~150μm) |
| Electrolysis | Anode metal dissolved and electrolytically deposited onto cathode | Wide distributions |
These techniques yield fine spherical, flaky or irregular particulate with controlled size distributions customizable across industry uses. Additional annealing, crushing, sorting, sieving achieves precise particle dimensions and purity.
On-site alloying entails mixing constituent metal powder according to formula, then consolidating them into net-shape components via compaction, 3D printing or injection molding. This simplifies logistics where specialized mixes are needed on smaller scales.
Applications of Copper Powder Alloys
Major industrial uses of copper alloy powder include:
| Application | Details |
|---|---|
| Surface Coatings | Thermal spray coatings, PVD, welding wires |
| Bushing and Bearing | Oil-free lubricity, embedability |
| Brazing Alloys | Joining agents for metals, ceramics |
| Injection Molded Parts | Net-shape small components |
| Press and Sinter Parts | Structural bushings, guides, sleeves |
| 3D Printing Filaments | Customizable grades for printers |
| EMI Shielding | Signal clarity in electronics |
| Diamond Tools | Binder matrix, aids cutting |
The unique thermal, electrical and mechanical properties of copper alloys serve critical needs from reducing friction in heavy machinery through enabling heat sinks in advanced electronics.
Copper Alloy Powder Specifications
Key parameters that characterize copper powder alloys:
| Attribute | Typical Values |
|---|---|
| Particulate shapes | Spherical, irregular, flaky |
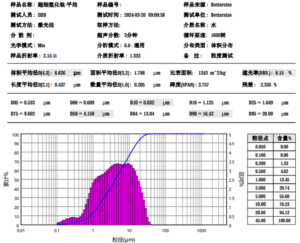
| Dimensions | 1 micron to 150 micron |
| Size distribution | Percentage under 10 μm, 53 μm etc. |
| Apparent density | Around 2-4 g/cm3 |
| Tap density | Up to around 70% of material density |
| Flow rates | Angle of repose < 40° |
| Oxide content | < 3% target |
| Contamination limits | < 1% by composition |
Specifying size distributions, purity levels, particulate geometry, apparent densities and flow rates ensures performance repeatability across production runs tailored for given fabrication process requirements.
Copper Alloy Powder Pricing
Price drivers for copper alloy particles are:
- Base metal market prices
- Purity grades
- Precise alloy ratios
- Specialty compositions
- Particulate sizes and distributions
- Order volumes and lot sizes
| Type | Price Range |
|---|---|
| Copper Powder | $5 – $15 per lb |
| Brass Powder | $6 – $25 per lb |
| Bronze Powder | $6 – $30 per lb |
| Copper Nickel Powder | $15 – $50 per lb |
Pricing also depends on production method – atomization is costlier but yields very spherical, purified powders suited for additive manufacturing for example. Quantify all parameters likeHours or content needed here to describe pricing nuances further.
Top Suppliers of Copper Alloy Powders
| Suppliers | Locaiton | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Makin Metal Powders | UK | Wide range of bronze, brass, copper powders |
| ACuPowder | US | Copper nickel, tin alloys |
| Shanghai CNPC | China | Brass, bronze, chrome copper powders |
| Hoganas | Sweden | Brazing, surface engineering alloys |
These major established powder metalwork vendors offer standard catalog alloys alongside ability to customize compositions and particulate specifications suitable for given production techniques and component performance requirements across global markets.
Copper Alloy Powder – Pros vs Cons
Advantages of copper particles:
- High electrical and thermal conductivity
- Corrosion resistance maintains longevity
- Antimicrobial properties prevent biofouling
- Softer than steel alloys, easily fabricated
- Reduces friction against mating surfaces
- Customizable ratios for desired properties
Tradeoffs with copper powder include:
- Generally heavier than competing alloys
- Material expense greater than steel or aluminum
- Oxidation risks with small particle sizes
- Heavier finishing needs for aesthetics
- Impacts aquatic organisms at densities above EPA thresholds
Understanding holistic lifecycle costs against alternatives like 316L stainless or aluminum balances useful strengths with long term value in use across target applications.

FAQ
Q: What are common copper alloy powders available?
A: Brass, bronze, copper-nickel and Nordic gold represent widely produced alloys balancing electrical, corrosion resistance, mechanical attributes.
Q: What particle sizes are typical for copper powder?
A: Particulate spans a wide range – from 1 micron powder suited for MIM pressing through 120 mesh flakes usable for thermal spray.
Q: How much does copper alloy powder cost?
A: Pricing ranges $5-15/lb for simple copper up to $50/lb for more exotic combinations, driven by base metal prices, purity, production method, order volumes.
Q: Where can I purchase specialty copper alloy powders?
A: Major powder metalwork vendors like Makin, Hoganas and ACuPowder enable custom particulate production alongside supplying common catalog grades.
Q: What safety precautions are necessary handling copper powders?
A: Requirements resemble other base metal powders – ventilation to control dust inhalation risks, grounded equipment to prevent static sparks, approved dust masks and gloves for contamination protection.