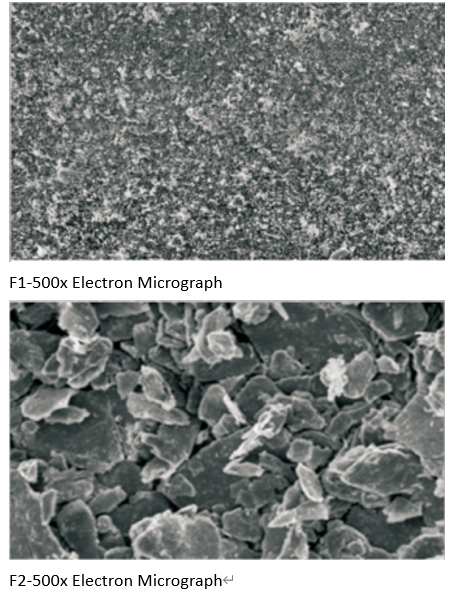
In the powder metallurgy industry, molybdenum disulfide is widely used as a friction-reducing additive,
and its excellent lubricity and stable chemistry ensure that the products effectively reduce wear during use, thus increasing product stability and service life.
Experimental objectives.
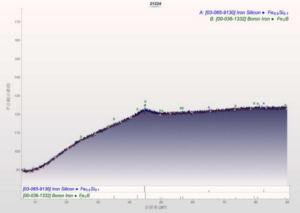
(1) Compare the difference in wear resistance of products by extrapolating the wear amount from the change in the internal diameter of the products.
(2) Check the wear of the product and compare the fit with other parts.
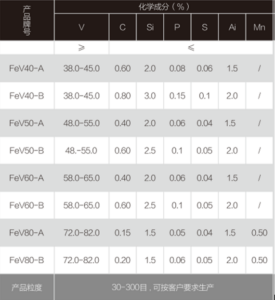
| Recommended specifications for powder metallurgy industry(Purity>98.0%) | |||
| Grades | F-1 | PF-2 | |
| Parameter(Max) | |||
| Acid insoluble substance(%) | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| Molybdenum trichloride(%) | 0.15 | 0.05 | |
| Silicon dioxide (SiO2)(%) | 0.10 | 0.10 | |
| Iron(%) | 0.25 | 0.30 | |
| Water(%) | 0.15 | 0.30 | |
| Oil(%) | 0.40 | 0.40 | |
| Carbon(%) | 0.50 | 0.50 | |
| Acid value | 0.50 | 0.50 | |
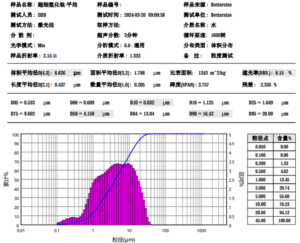
| particle size | D50μm | 1.5 | 12-16 |
| D90μm | — | 45 | |
| D100μm | 10 | — |
Experimental Conclusions
(1) Product wear resistance: the product with molybdenum disulfide has better wear resistance.
(2) Matching between products and other parts; products with molybdenum disulfide additions have better matching with other parts.
.jpg)