Spheroidization Rate and Spheroidal Grade of Graphite in Ductile Cast Iron.
The spheronization rate and spheronization grade are assessed according to GB/T9441-1988 “Ductile Iron Metallographic Inspection”, which divides the spheronization grade into 6 grades. Firstly, the whole inspected surface is observed, and then, starting from the worst area, 5 fields of view are observed consecutively, and the majority of 3 of the worst fields of view are evaluated against the grade spectrum.
The key to improving sphericity is spheronization and conception treatment.
Spheroidization treatment method: the use of rare earth magnesium alloy pit punching method, simple and easy, but the soot is larger. The use of low rare earth magnesium alloy cover package treatment, magnesium yield up to more than 50% and can solve the problem of soot.
Conception treatment can be used two or three conceptions, spherical bag inoculant can be used 75 ferrosilicons, the pouring bag can be added anti-decline (such as containing barium) inoculant. If necessary, in-current or intra-pregnancy is used.
Both grade 5 and grade 6 spheroid graphite are dominated by worm-like graphite, with grade 5 spheroid being a dispersion of worm-like graphite and grade 6 spheroid being an aggregation of worm-like graphite. The main differences between the two are as follows.
(1) Macroscopic organization When the aggregated distribution, a sparse number of small black spots appear on the fracture, when the worm-like graphite aggregation increases, the black spots increase, the number also increases and densely; worm-like graphite scattered distribution, the number of less than the aggregated distribution, the fracture will not appear small black spots.
(2) microscopic characteristics of worm-like graphite scattered distribution, its length and width are relatively small, was short and coarse rod-shaped, rounded blunt end, often coexist with clusters. 4 to 5 worm-like graphite clustered at one place, known as the aggregated distribution, this time the worm-like graphite bending, twisting tendency to increase. Observe the three-dimensional morphology, the aggregated distribution of several worm-like graphites is often the same worm-like graphite of different branches, this structure, the specific surface area is larger, the distance between the branches and branches is closer, is conducive to the diffusion of carbon, so the casting state or after heat treatment, the aggregated distribution of worm-like graphite around the formation of ferrite easily.
(3) Chemical composition When the worm-like graphite is aggregated and distributed, the amount of residual magnesium and rare earth in the macro-chemical composition are low, and the amount of silicon is high.
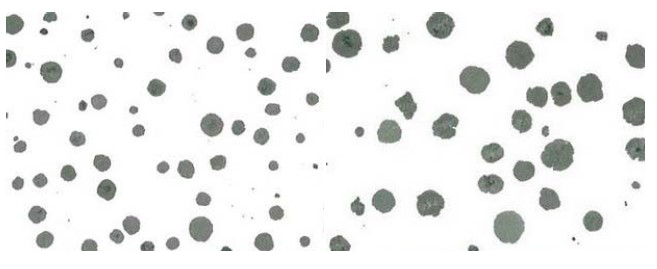
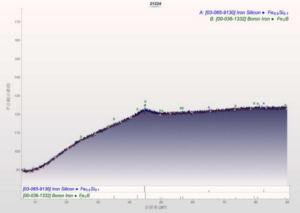
Number:01
Optical Magnification: 100x
Erosion agent: None
Material and Condition:nodular graphite cast iron
Process: casting
Organization and description: The graphite in the figure is spherical, a few clusters, the sphericity is ≥95%, and the sphericity grade is Grade 1.
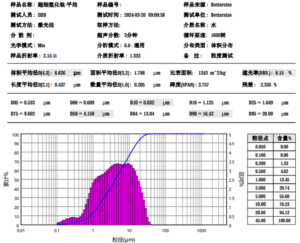
Number:02
Optical Magnification: 100x
Erosion agent: None
Material and Condition: nodular graphite cast iron
Process: casting
Organization and Description: Most of the graphite in the figure is spherical, the rest is clusters or very few clusters flocculents, the spheroidization rate is 90%-<95%, the spheroid level is 2 grade.
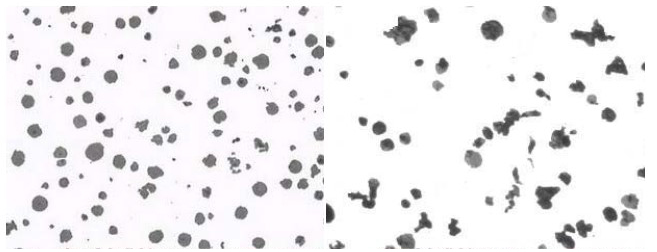
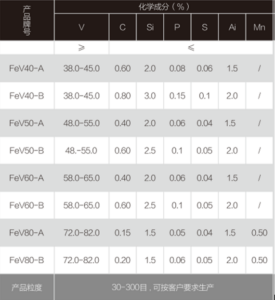
Number:03
Optical Magnification: 100x
Erosion agent: None
Material and Condition: nodular graphite cast iron
Process: casting
Organization and Description: Most of the graphite in the figure is agglomerated and spherical, the rest is agglomerated flocculent, the spheroidal rate is 80%-<90%, the spheroidal grade is 3.
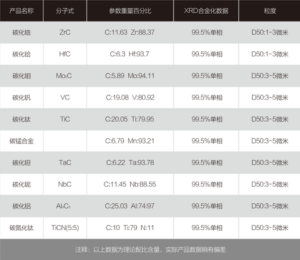
Number 04:
Optical Magnification: 100x
Erosion agent: None
Material and Condition: nodular graphite cast iron
Process: casting
Organization and description: most of the graphite in the figure is flocculent and spherical, a small amount of worm-like, spheroidal rate of 70%-<80%, spheroidal grade 4.